链表是否存在环?
描述
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
思路
使用两个指针,一个每次走两步,一个每次走一步,如果一段时间之后这两个指针能重合,那么链表就存在环了。 但是,这不是一个充要条件,两个指针相遇,我们可以通过反证法轻易证明链表存在环;链表存在环,两个指针就一定会相遇吗?
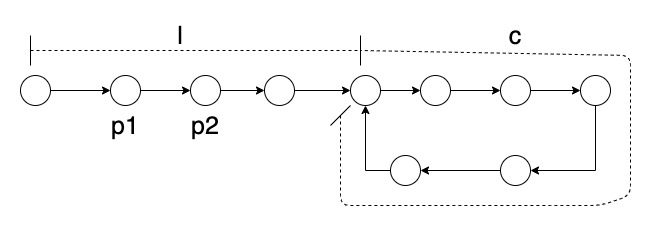
现在就来证明一下吧。
如图,我们记环开始前的距离为 l,环长为 c, p1 前进的距离为 f1(t),p2 前进的距离为 f2(t),t 表示时间。
要证明两个指针相遇,等价于证明:
存在正整数 t 和 n,使得
f2(t) - f1(t) = n * c,且f2(t) - f1(t) >= l,其中f2(t) = 2 * tf1(t) = t
当 c >= l 时,取 t = c, n = 1 即可满足上述命题;
当 c < l 时,取 t = ceil(l / c) * c, n = ceil(l / c),其中 ceil表示向上取整, 即可满足上命题
解答
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
if not head or not head.next:
return False
p1, p2 = head, head.next
while not (p1 is p2) and (p2 and p2.next and p2.next.next):
p1 = p1.next
p2 = p2.next.next
if p1 is p2:
return True
return False